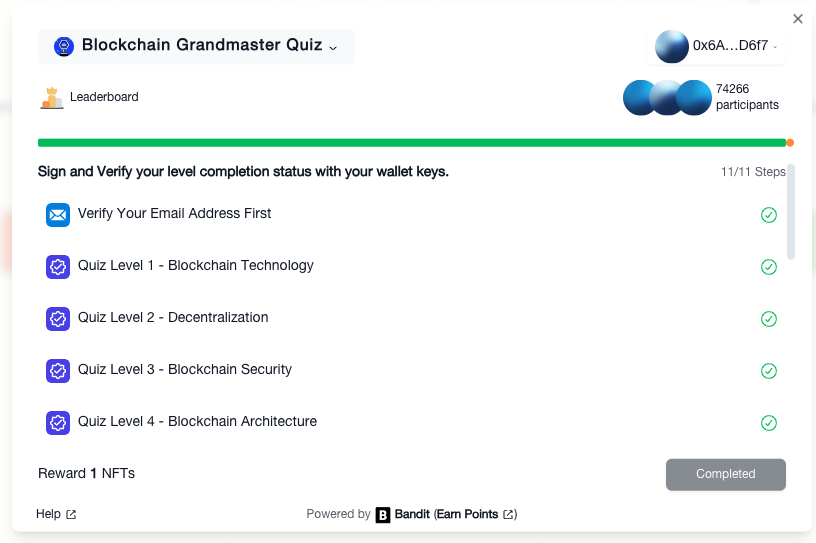
Blockchain Grandmaster Quiz to Claim NFT
Link to Quizzes – https://shardeum.org/explore/blockchain-grandmaster-quiz/#
Shardeum Discord: https://discord.gg/77Ydmh3MaF
Quiz Answers May Not Show in the Same Order – so “CTRL” + F & paste the question to find it faster
👉 Level 1 – Blockchain Grandmaster
- What type of digital ledger and database is blockchain technology?
- D. Permissionless/Decentralized & DLT
- What is the unique identifier for a block in a blockchain called?
- C. Block Hash
- Which of the following is a layer 1 blockchain platform/network?
- C. Ethereum
- Which of the following represent the bedrock principles of a public blockchain?
- C. Decentralization, Security, Immutability & Transparency
- Which of the following is NOT a consensus mechanism used in typical blockchain networks?
- A. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
- What is the purpose of a merkle tree in a blockchain?
- D. All of the above
- Nonces in ____ network are used to create unique identifiers for transactions to prevent double-spending/replay attacks but are NOT used to determine the selection of validators.
- D. All of the above
- Which of the following best describes a “block” in a blockchain?
- A. A group of transactions ordered, validated, confirmed and added to a blockchain
- What is the core problem that blockchain solves?
- B. Secure data validation and storage without a 3rd party
- Which of the following is not a decentralized/public blockchain network?
- B. Hyperledger Fabric
👉 Level 2 – Decentralization
- Which of the following does NOT represent decentralization in the Decentralized Finance or DeFi industry?
- B. Stability and security enabled by banks
- Which of the following is the primary benefit of decentralization in the context of censorship resistance?
- C. Reduced reliance on intermediaries
- Which of the following best describes how decentralization operates in blockchain networks?
- B. By distributing control and resources among many unrelated nodes across the world
- What is the benefit of decentralization in blockchain networks?
- D. All of the above
- Which is the most significant indicator of a highly decentralized blockchain/Web3 network?
- C. Network with several independent nodes spread across the world
- What are three primary types of blockchain clients?
- A. Lightweight or SPV clients, Full clients, and Archive clients
- Which decentralized technology allows users to access web content and services without relying on traditional domain names and centralized DNS?
- D. IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
- Which of the following best describes a blockchain “client”?
- C. Software that enables interaction with a blockchain while upholding the network’s operational protocols
- Which of the following is what makes it possible for a group of strangers to work together to build and maintain a shared database like blockchain, without needing to trust each other?
- D. Consensus mechanism
- Which blockchain consensus mechanism promotes decentralization by allowing any participant to contribute to the network’s security and governance, albeit, by using expensive and powerful hardware?
- A. Proof of Work (PoW)
👉 Level 3 – Blockchain Security
- Beyond the consensus mechanism, which of the below is the most ideal technique sharded blockchains can employ to maintain the high security levels that public blockchains are known for?
- A. Auto-rotation of nodes
- What is the primary reason for keeping a safe backup of your passphrase (or seed phrase/backup codes) when using blockchain wallets, even though other security measures mentioned here may also apply?
- A. To recover your account if you lose your private keys
- Asides from hashing, which other key cryptographic method does blockchain technology employ to ensure that data doesn’t change during the broadcast of validated transactions between nodes and throughout all blockchain transactions for that matter?
- C. Digital signatures
- How can Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks, such as Ethereum, achieve a security level comparable to that of Proof-of-Work (PoW) networks like Bitcoin?
- B. Through a system where validators stake assets as collateral
- Safe deposit boxes (or bank lockers) are secured by a key that only the owner (custodians like banks) have access to. Similarly, what protects digital assets owned by users themselves on a blockchain?
- C. A pair of public and private keys
- As modern blockchain networks strive to reduce transaction fees, which attack type lets attackers cheaply flood the network with low cost requests to slow/disrupt it?
- D. DDoS attack
- Consider a malicious attacker creating multiple pseudonymous identities by taking control over a node or group of nodes. These nodes are then used to spread misinformation, disrupt consensus, or attempt to influence the network’s decisions. What is the nefarious act known as in the context of blockchain?
- A. Sybil attack
- Which is the most battle-tested, highly secure hashing algorithm used by various blockchain networks to handle transactions and record data?
- D. SHA-2 and SHA-3
- Why do experts often emphasize addressing security issues at Layer 1 of a blockchain rather than relying solely on Layer 2 blockchains and other scaling solutions?
- C. Layer 1s is the foundational layer known to provide a very high level of security and decentralization, benefitting the entire network and all dapps built upon it
- Which term is commonly associated with the practice of prioritizing certain transactions on a blockchain by reordering them for potential financial gains, especially in the context of DeFi platforms?
- C. MEV (Miner Extractable Value)
👉 Level 4 – Blockchain Architecture
- What is the role of Virtual Machines like Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) in blockchain architecture?
- D. All of the above
- What type of blockchain network or platform allows anyone to participate in running nodes, anyone can read from or write to and is permissionless?
- C. Public blockchain
- Which key property in blockchain helps it to achieve both these desired outcomes – high fairness and prevent double-spending?
- A. Timestamp
- In the Ethereum blockchain, if someone were describing the overall structure and various levels of data organization, which of the following statements is accurate?
- C. The ‘Global State’ represents the entire state of the blockchain at a given moment, the ‘Current State’ emphasizes its latest status, the ‘Account State’ pertains to individual balances, nonces, and related data for Ethereum addresses, and the ‘Contract State’ refers to the specific code and storage for smart contracts
- Which statement accurately describes the relationship between ERC standards (Ethereum request for Comments) and EIPs in the Ethereum ecosystem?
- B. ERC standards, like ERC-20 and ERC-721, are types of EIPs that specifically define token standards on Ethereum
- Choose the correct answer. Which consensus algorithms are used by L1 blockchains, Bitcoin and Ethereum respectively?
- B. Bitcoin – Proof of Work (PoW), Ethereum – Proof of Stake (PoS)
- In which layer of blockchain architecture do smart contracts and dapps primarily operate while the end users directly interact with?
- A. Application Layer
- What is the primary purpose of improvement proposals or blockchain standards like EIP or BIP (Ethereum/Bitcoin Improvement Protocols) in the Ethereum/Bitcoin ecosystem?
- D. B & C
- Which of the following reasons explains why specialized sandbox environments called testnets or test networks are crucial for blockchain platforms?
- C. They provide environments to simulate the blockchain network for testing purposes before deploying on the mainnet, which involves real world value
- What is the primary purpose of a smart contract in a blockchain network?
- D. Automatically executing predefined instructions when specific conditions are met
👉 Level 5 – Blockchain Features
- Which feature in blockchain ensures that once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed?
- D. Finality
- What is a primary consequence of a blockchain network relying on high staking requirements and increased processing power (vertical scalability) while having limited throughput and scalability?
- D. Network congestion leading to high and unpredictable fees for end users
- In public blockchains, what permanent consequence occurs when validators fail to achieve consensus on the upcoming blocks or transactions to be appended?
- A. The blockchain splits into two separate chains (hard fork)
- “Blockchain trilemma” or “Scalability trilemma,” is a longstanding issue that hinders the mass adoption of blockchain networks. Which three features are encompassed by this trilemma in public blockchains?
- A. Security, decentralization and scalability
- Which of the following best describes the average transactions per second (TPS) comparison between a centralized network like Visa and typical public blockchain networks?
- A. Visa processes significantly more transactions per second than public blockchain networks
- Which feature addresses the potential of a public blockchain to handle increased transaction loads?
- D. Scalability
- Why is high fairness important in a blockchain network?
- B. It prevents certain participants from gaining undue advantage by manipulating transaction order
- Which feature of blockchain and smart contract platform represents this statement “A decentralized exchange (DEX) can be combined with a decentralized lending protocol to create a new application that allows users to borrow and lend assets while also trading them.”
- D. Atomic Composability
- Which feature ensures that transactions on the blockchain are processed quickly?
- C. Throughput
- Which of the below is an ideal and a highly decentralized solution for scalability issues in public blockchains?
- B. Adding more low end machines/nodes
👉 Level 6 – Blockchain Nodes
- What is the most accurate statement with respect to consensus mechanisms in sharded blockchain networks?
- A. Each shard reaches consensus on its own transactions
- In Filecoin, a decentralized storage platform, which type of nodes offer storage capacity, furnish cryptographic evidence of their reliable data storage, and swiftly deliver stored data to users when requested?
- B. Storage & Retrieval nodes
- What type of nodes provide an interface between traditional web browsers and IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), a decentralized storage network?
- D. Gateway nodes
- What type of nodes typically store the complete blockchain transaction history while maintaining the blockchain’s historical data as well?
- C. Archive nodes
- Which nodes are primarily responsible for actively participating in the process of ordering and validating transactions, forming consensus, proposing a block, and securing the network in PoS networks?
- B. Validator nodes
- In a blockchain network, which type of nodes provides interfaces for querying and interacting with the blockchain without the need to store the full transaction history?
- C. RPC Nodes
- What type of nodes typically store the complete blockchain transaction history while maintaining the current state of the ledger?
- D. Full nodes
- Which of the following best describes the role of blockchain client software for nodes?
- B. Allows nodes to operate, validate transactions, and maintain consensus on the blockchain network
- Which nodes are known to facilitate data transmission and propagation across PoS networks including sharded and cross-chain networks?
- A. Relay nodes
- What are nodes in a blockchain network?
- A. Participants or computers that order, validate, relay, and store transactions and blocks in the network
👉 Level 7 – Blockchain Infrastructure & Components
- Which of the following are considered to be part of blockchain infrastructure?
- D. All of the above
- In the evolving landscape of blockchain infrastructure, how do decentralized storage networks differentiate themselves from traditional data storage mechanisms?
- C. By fragmenting data into chunks and distributing them across nodes, ensuring redundancy and resistance to censorship without centralized control
- Why are development tools/frameworks like Truffle, Hardhat and Anchor essential for blockchain development
- A. They are back-end tools for developers to test/deploy smart contracts and dapps seamlessly to deliver decentralized products and services for end users
- Which of the following popular software clients are used for interacting with the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains respectively?
- A. Bitcoin – Bitcoin Core, Ethereum – Geth
- What necessitated layer 2 blockchains and solutions on top of layer 1 blockchains?
- D. All of the above
- Which of the following best describes the difference between on-chain and off-chain solutions in the context of blockchain technologies?
- B. On-chain solutions pertain to data and transactions stored directly on the main blockchain, while off-chain solutions involve data and transactions processed outside of the blockchain
- What is the primary role of a wallet in blockchain?
- B. Acting as a bridge between users and the blockchain network
- How does a “wallet” primarily interface with the blockchain network
- B. By allowing users to create and broadcast transactions using cryptographic keys
- In the context of blockchain technology, what primary role do websockets play?
- C. Real-time event listening and data updates
- Which of the following is not considered a layer 2 solution in blockchain?
- A. Sharding
👉 Level 8 – Smart Contracts
- How exactly did Ethereum elevate the potential of blockchain technology pioneered by Bitcoin? Choose the correct answer.
- B. Ethereum revolutionized the way real-world applications function by introducing smart contracts and decentralized applications, eliminating the need for intermediaries
- Which of the following options represent the primary challenge for smart contracts and the larger blockchain industry as a whole?
- C. Smart contracts are vulnerable to bug and other flaws in the code resulting in security breaches and loss of funds
- What are the benefits of using smart contracts to manage supply chains?
- D. All of the above
- Which of the following best describes a complex smart contract?
- A. A contract that autonomously performs a series of actions based on external data inputs and has multiple conditional outcomes.
- Which of these is NOT a use case for smart contracts?
- B. Real-time weather updates
- In the context of Ethereum dapp development, how is the Solidity programming language best characterized?
- C. Smart contract programming language
- What is the term used to refer to the fee paid by end users to execute a function in a smart contract such as transferring tokens, voting in a DAO or minting an NFT?
- C. Gas Fee
- What is the significant advantage of using oracles in smart contracts?
- A. Allow contracts to retrieve external world data
- Which of the following is the MOST accurate definition of gas estimate and gas limit?
- A. Gas estimate is the estimated amount of gas that a transaction will require, while gas limit is the maximum amount of gas that a user is willing to spend on a transaction
- How are smart contract vulnerabilities typically exploited?
- D. By taking advantage of poorly written contract code
👉 Level 9 – Dapps
- In a dapp, what is the role of a ‘token’?
- D. All of the above
- Which of the following does not operate as a decentralized application (dapp)?
- B. iPhone App Store
- What is the main distinction between smart contracts and dapps (Decentralized Applications)?
- D. Smart Contracts facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract, while dapps are the front-end interface of smart contracts
- How can dapps be described in terms of governance?
- B. They are usually governed by consensus among network participants
- Which of the following is a use case of decentralized application (Dapp)?
- C. Automated Market Maker (AMM)
- Which of the following platforms does NOT function both as a Layer 1 (L1) blockchain and as a smart contract platform enabling decentralized solutions and applications for end users?
- A. Bitcoin
- Which component in a dapp ensures that it can operate without a central authority?
- C. Smart Contracts
- On which of the following factors does a dapp’s performance primarily depend?
- C. Performance of the underlying (L1) blockchain
- Which layer on a L1 blockchain does smart contracts and dapps typically reside?
- A. Smart Contracts and dapps reside in the same application layer since smart contracts are simply the backend logic for dapps
- Which term refers to a collection of smart contracts that act as a back-end with a front-end user interface?
- A. Decentralized Application (Dapp)
👉 Level 10 – Blockchain Interface & Utilities
- Which statement best describes the differences among lightweight wallets, full-node wallets, and third-party wallet applications in the context of blockchain?
- C. Lightweight wallets don’t store the entire blockchain but allow transactions, full-node wallets store and verify the entire blockchain, and third-party wallets are applications developed by external entities to manage keys and transact.
- What role does a blockchain explorer play in the blockchain ecosystem?
- D. It enables users to view detailed information about blocks, transactions, and addresses
- What is the common objective that blockchain bridges, atomic swaps, and synthetics aim to achieve in the Web3 ecosystem?
- B. Facilitate seamless interactions or value transfer across different blockchains
- _____ platforms aggregate and interpret vast amounts of on-chain data to produce useful metrics and insights about network health, economic activity, market sentiment, and more.
- B. On-chain Analytics
- Which (Ethereum) Layer-2 scaling solution utilizes zero-knowledge proofs to cryptographically ensure every transaction’s correctness without requiring fraud verification windows or challenge periods?
- D. zk-Rollups
- What is the use case of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (zk-proofs) technology in blockchain?
- D. All of the above
- Which Ethereum Layer-2 scaling solution processes transactions off-chain assuming them to be correct unless proven otherwise requiring a dispute resolution window?
- C. Optimistic Rollups
- Why are oracles considered an important blockchain interface?
- A. They allow blockchains and its smart contracts to interact with external data sources
- _____ are blockchain systems that run parallel to a “mainchain” or L1 blockchain providing a mechanism to offload transactions from the mainchain, while performing their own consensus mechanism to reduce congestion and allow for faster processing times and interoperability.
- D. Sidechains
- Which of the following best describes the primary function of the MetaMask web browser extension?
- C. A wallet interface for interacting with Ethereum-based dapps
👉 claim your NFT